Editor’s note: The following is extracted from Heroes of Modern Europe, by Alice Birkhead (published 1913). All spelling in the original.
The year of Revolution, beginning with most glorious hopes, ended disastrously for the Italian patriots. Princes had allied with peasants in eager furtherance of the cause of freedom but defeat took away their faith. The soldiers lost belief in the leaders of the movement and belief, alas! in the ideals for which they had been fighting.
Charles Albert, the King of Sardinia, continued to struggle on alone when adversities had deprived his most faithful partisans of their zeal for fighting. He had once been uncertain and vacillating in mind, but he became staunch in his later days and able to reply courageously to the charges which his enemies brought against him. He mustered some 80,000 men and put them under Polish leaders—a grave mistake, since the soldiers were prejudiced by the strange foreign aspect of their officers and began the war without enthusiasm for their generals.
Field-Marshal Radetsky, a redoubtable enemy, only brought the same numbers to the field, but he had the advantage of being known as a conquering hero. His cry was “To Turin!” but the bold Piedmontese rallied to defend their town and spread the news of joyful victory throughout the Italian peninsula. Other defenders of liberty dared to raise their heads now, thought once more of Italy free and united.

At the battle of Novara, fought on an April morning of 1849, the King of Sardinia gave up his throne, and longed for death that he might make some tardy recompense for the failure of his attempt to withstand the power of Austria. “Let me die, this is my last day,” he said when officers and men would have saved him from the fate of the 4000 Sardinians who lay dead and wounded. He was not suffered to meet death but rode away, pointing to his son Victor Emmanuel II as he left his army. “There is your King!” he said, resigning all claim to royalty now that he had met defeat. He promised that he would serve in the ranks as a private soldier if Italian troops made war again on Austria.
After the disgrace of Novara and the flight from Rome it seemed that Mazzini could do nothing more for the cause of patriotism he had served so nobly. He had given up hope of a great Italian Republic, and saw that men’s hearts were turned toward the young King Victor and the monarchy.


Yet Garibaldi, the soldier of fortune, had not renounced the aspirations of Mazzini, a leader to whom he had always been devoted. “When I was young I had only aspirations,” he said. “I sought out a man who could give me counsel and guide my youthful years; I sought him as the thirsty man seeks water. This man I found; he alone kept alive the sacred fire; he alone watched while all the world slept; he has always remained my friend, full of love for his country, full of devotion for the cause of freedom: this man is Joseph Mazzini.”
The worship of the prophet had led the gallant, daring sailor into hairbreadth escapes and strange vicissitudes of fortune. He had been sentenced to death as “an enemy of the State and liable to all the penalties of a brigand of the first category.” He had fled to South America and ridden over the untrodden pampas, tasting the wild life of Nature with a keen enjoyment. He had been a commander in the navy, and had defended Monte Video. He had been imprisoned and tortured, and had taken Anita, daughter of Don Benito Riverio de Silva of Laguna to be his wife and the companion of his adventures.
Garibaldi could not afford even the priest’s marriage fees for his life was always one of penury, so he gave him an old silver watch. When he was Head of the Italian Legion he was content to sit in the dark, because he discovered that candles were not served out to the common soldiers. The red shirts of his following had been bought originally for their cheapness, being intended for the use of men employed in the great cattle-markets of the Argentine. The sordid origin of the Camicia Rossa was soon forgotten as it became the badge of honour. Its fame was sung in many foreign lands, and it generally figured in pictures of Garibaldi.
The Legion created some alarm in Rome as they appeared—men with their dark faces surmounted by peaked hats and waving plumes. Garibaldi himself rode on a white horse and attracted favourable notice, for he was a gallant horseman and his red shirt became him no less than the jaunty cap with its golden ornaments. Three thousand men accepted the offer which the chief made when there was news that the French were advancing to the city. He did not promise them gold nor distinction, but a chance of meeting their ancient enemy of Austria. Cold and hunger would be theirs, and the weariness of constant marches. Death would be the lot of many in their ranks, the cruel tortures of their gaolers. All men were outlaws who had defended Rome, the Republic, to the last, and bread and water might be refused to them within the confines of their country.

The cry for war sounded, and Garibaldi led three thousand men, including Ugo Bassi and the noblest of knight-errants. The attempt to reach Venice was frustrated by a storm, and Anita died miserably in a peasant’s cottage, where she was dragged for shelter. Garibaldi fled to the United States, and never saw again many of his bold companions. Venice was left of dire necessity to defend herself from Austria. She had sworn to resist to the last, and President Manin refused to surrender even when cholera came upon the town and the citizens were famished. He appealed to England, but only got advice to make terms with the besiegers. He capitulated in the end because the town was bombarded by the Austrian army, and he feared that the conquerors would exercise a fell vengeance if the city still resisted. There was nothing left to eat after the eighteen months’ siege of Venice. Manin left for Marseilles, mourned bitterly by the Venetians. His very door-step was broken by the Austrians, who found his name upon it. Ugo Bassi had kissed it, voicing the sentiment of many. “Next to God and Italy—before the Pope—Manin!”

Victor Emmanuel, the young King of Sardinia, had won no such popularity, suffering from the prejudice against his family, the House of Savoy, and against his wife, an Austrian by birth. He came to the throne at a dark time, succeeding to a royal inheritance of ruin and misery. The army had been disgraced, and the exchequer was empty. He had the dignity of a king and remarkable boldness, but it would have been hard for him to have guided Italy without his adviser and friend, the Count Cavour.
Mazzini, the prophet, and Garibaldi, the soldier, had won the hearts of Italians devoted to the cause of Italy. Cavour suffered the same distrust as Victor Emmanuel, but he knew his task and performed it. He was the statesman who made the government and created the present stable monarchy. He had to be satisfied with less than the Republican enthusiasts. He had few illusions, and believed that in politics it was possible to choose the end but rarely possible to choose the means.
Born in Piedmont in 1810, the statesman was of noble birth and sufficient wealth, being a godson of Pauline, sister of the great Napoleon. He joined the army as an engineer in 1828, but found the life little to his taste since he was not allowed to express his opinions freely. He resigned in 1831 and retired to the country, where he was successful as a farmer. He travelled extensively for those days, and visited England, where he studied social problems.

Of all foreigners, Cavour, perhaps, benefited most largely by a study of the English Parliament from the outside. He was present at debates, and wrote articles on Free Trade and the English Poor Law. He had enlightened views, and wished to promote the interests of Italy by raising her to the position of a power in Europe. He set to work to bring order into the finances of Sardinia, but the King recognized his minister’s unpopularity by the nickname bestia neira. He had a seat in 1848 in the first Parliament of Piedmont, and was Minister of Commerce and Agriculture later. He pushed on reforms to benefit the trade and industries of Italy without troubling to consult the democrats, his enemies. His policy was liberal, but he intended to go slowly. “Piedmont must begin by raising herself, by re-establishing in Europe as well as in Italy, a position and a credit equal to her ambition. Hence there must be a policy unswerving in its aims but flexible and various as to the means employed.” Cavour’s character was summed up in these words. He distrusted violent measures, and yet could act with seeming rashness in a crisis when prudence would mean failure.
Prime Minister in 1852, he saw an opportunity two years later of winning fame for Piedmont. The Russians were resisting the western powers which defended the dominions of the Porte. Ministers resigned and the country marvelled, but Cavour signed a pledge to send forces of 15,000 men to the Crimea to help Turkey against Russia. It would be well to prove that Italy retained the military virtues of her history after the defeat of Novara, he said in reply to all expostulations. The result showed the statesman’s wisdom and justified his daring. The Sardinians distinguished themselves in the Crimea, and Italy was able to enter into negotiations with the great European powers who arranged the Peace of Paris.
The Congress of Paris was the time for Cavour to gain sympathy for the woes of Italian states, still subject to the tyrannous sway of Austria. He denounced the enslavement of Naples also, and brought odium upon King Ferdinand, but “Austria,” he said, “is the arch-enemy of Italian independence; the permanent danger to the only free nation in Italy, the nation I have the honour to represent.”

England confined herself to expressions of sympathy, but Louis Napoleon, now Emperor of France, seemed likely to become an ally. He met Cavour at Plombières, a watering place in the Vosges, in July 1858, and entered into a formal compact to expel the Austrians from Italy. The final arrangements were made in the following spring in Paris. “It is done,” said Cavour, the minister triumphant. “We have made some history, and now to dinner.”
Mazzini, in England, read of the alliance with gloomy misgivings, for, as a Republican, he distrusted the President of France who had made himself an Emperor. He said that Napoleon III would work now for his own ends. He protested in vain. Garibaldi rejoiced and returned from Caprera, where he had been trying to plant a garden on a barren island.
Cavour fought against some prejudice when he offered to enrol Garibaldi and his followers in the army of Sardinia. Charles Albert had refused the hero’s sword in the days of his bitter struggle, and the regular officers still looked askance on the Revolutionary captain.
But the Austrian troops were countless, numbering recruits from the Tyrol and Bohemia, from the valleys of Styria and the Hungarian steppes. There was need of a vast army to oppose them. The French soldiers fought gallantly, yet they were inferior to the Austrians in discipline. When the allies had won the hard contested fight of Montebello it was good to think of that band of 3000, singing as they marched, “Addio mia bella, addio,” like the knights of legend. They crossed Lake Maggiore into the enemy’s own country, and took all the district of the Lowland Lakes.
In June, the allies won the victory of Magenta, and on the 8th of that month, King and Emperor entered Milan flushed with victory. The Austrians had fled, and the keys of the city were in the possession of Victor Emmanuel.

The Emperor of Austria, Francis Joseph, had assumed command of the army when the great battle of Solferino was fought amidst the wondrous beauty of Italian scenery in an Italian summer. It was June 24th, and the peasant reaped the harvest of Lombardy, wondering if he should reap for the conqueror the next day. The French officers won great glory as they charged up the hills, which must be taken before they could succeed in storming Solferino. After a fierce struggle of six hours, the streets of the little town were filled with the bodies of the dead and dying. By the evening, the victory of the allies over Austria was certain.

Napoleon III had kept his promise to the Italian people, who were encouraged by a success of the Piedmontese army under Victor Emmanuel at San Martino. But he disappointed them cruelly by stopping short in his victorious career and sending General Fleury to the Austrian camp to demand an armistice. Europe was amazed when the preliminaries of peace were signed, for it was generally expected that Austria would be brought to submission. Italy was in despair, for Venetia had not yet been won for them.
Cavour raged with fury, regretting that he had trusted Napoleon and trusted his King, Victor Emmanuel, who agreed to the proposals for an armistice. Now he heaped them with reproaches because they had given up the Italian cause. He resigned office in bitterness for it was he who had concluded the alliance of France and Italy.
Napoleon returned to France, pursued by the indignation of the country he had come to deliver. He complained of their ingratitude, though he might have known that Lombardy would not accept freedom at the cost of Venice. He was execrated when the price of his assistance was demanded. France claimed Nice and Savoy as French provinces henceforth. Savoy was the country of Victor Emmanuel, and Nice the honoured birthplace of the idolized Garibaldi!
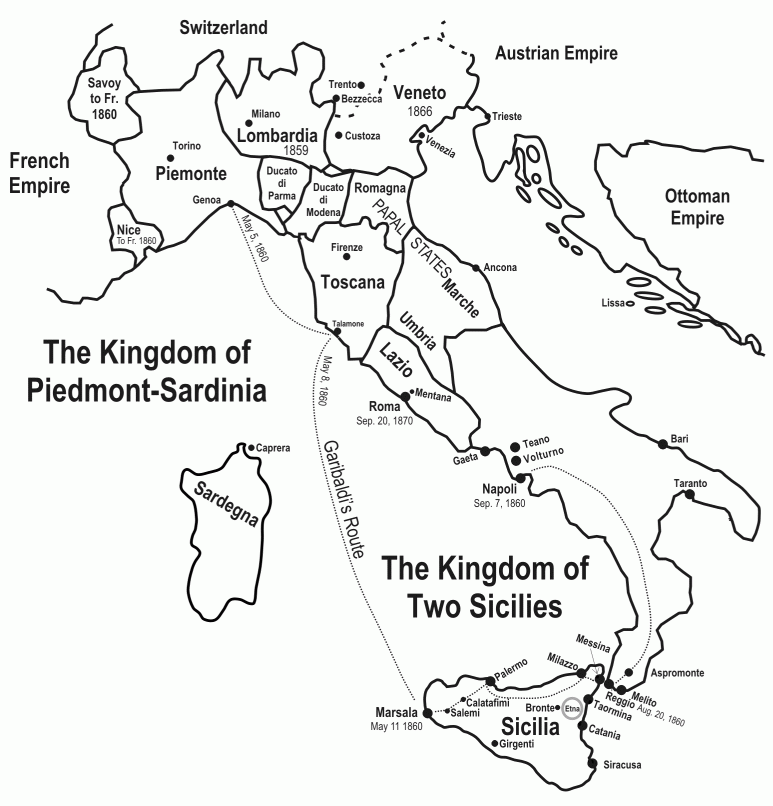
Garibaldi was chosen by the people of Nice for the new Chamber of 1860, for they hoped that he would make an effort to save his native town. He had some idea of raising a revolution against French rule, but decided to free Sicily as a mightier enterprise. Victor Emmanuel completed the sacrifice which gave “the cradle of his race” to the foreigner. He was reconciled to the cession at length because he believed that Italy had gained much already.
Cavour did not openly approve of the attack which Garibaldi was preparing to make upon the Bourbon’s sovereignty. Many said that he did his best to frustrate the plans of the soldier because there was hostility between them. Garibaldi could not forgive the cession of Nice to which the statesmen had, ere this, assented. He was bitter in his feeling toward Victor Emmanuel’s minister, but he was loyal to Victor Emmanuel. His band of volunteers, known as the Thousand, marched in the King’s name, and the chief refused to enrol those whose Republican sentiments made them dislike the idea of Italian unity. “Italy and Victor Emmanuel,” the cry of the Hunters of the Alps, was the avowed object of his enterprise.

Garibaldi sailed amid intense excitement, proudly promising “a new and glorious jewel” to the King of Sardinia, if the venture were successful. The standard of revolt had already been raised by Rosaline Pilo, the handsome Sicilian noble, whose whole life had been devoted to the cause of country. The insurgents awaited Garibaldi with a feverish desire for success against the Neapolitan army, which numbered 150,000 men. They knew that the leader brought only few soldiers but that they were picked men. Strange stories had been told of Garibaldi’s success in warfare, being due to supernatural intervention. The prayers of his beautiful old peasant-mother were said to have prevailed till her death, when her spirit came to hold converse with the hero before battle.

The Red-shirts landed at Marsala, a thousand strong, packed into merchant vessels by a patriotic owner. Garibaldi led them to the mountain city of Salemi, which had opposed the Bourbon dynasty warmly. There he proclaimed himself dictator of Sicily in the name of Victor Emmanuel, soon to be ruler of all Italy. Peasants joined the Thousand, armed with rusty pistols and clad in picturesque goat-skins. They were received with honour by the chief, who was pleased to see that Sicily was bent on freedom. A Franciscan friar threw himself upon his knees before the mighty leader and asked to join the expedition. “Come with us, you will be our Ugo Bassi,” Garibaldi said, remembering with a pang the defence of Rome and the fate of the defenders.
At Palermo, the capital of Sicily, the Neapolitan soldiers were awaiting the arrival of the Thousand. They ventured to attack first, being very strong in numbers. The bravest might have feared to oppose the royal troops with such a disadvantage, but Garibaldi held firm when there were murmurs of surrender. “Here we die,” he said, and the great miracle was accomplished. “Yesterday we fought and conquered,” the chief wrote to the almost despairing Pilo. The two forces joined and Pilo fell, struck by a bullet. It was May 27th when Garibaldi entered the gates of Palermo.
The bells were hammered by the inhabitants, delighted to welcome the brave Thousand to their city. There was still a fierce struggle within the walls, and the Neapolitan fleet bombarded the town. An armistice was granted on May 30th, for the Royalists needed food and did not realize that Garibaldi’s ammunition was exhausted. He refused to submit to any humiliating terms that might be offered to Palermo. He threatened to renew hostilities if the enemy still thought of them. All declared for war, though they knew how such a war must have ended. It was by the Royalists’ act that the evacuation of the city was concluded.
The Revolution had succeeded elsewhere, and for the last time the Bourbon flag was hoisted in Sicilian waters. The conquest of Sicily had occupied but a few days. The Dictator proceeded thence to the south of Italy and advanced on the Neapolitan kingdom.
Victor Emmanuel would have checked the hero of Palermo, and Cavour was thoroughly uneasy. No official consent had been given for this daring act of aggression, and foreign powers wrote letters of protest, while King Francis II, the successor of Ferdinand, held out such bribes as fifty million francs and the Neapolitan navy to aid in liberating Venice. France induced the King of Sardinia to make an effort to restrain the popular soldier. Garibaldi promised Victor Emmanuel to obey him when he had made him King of Italy.

At Volturno the decisive battle was fought on the first day of October 1860, the birthday of King Francis. “Victory all along the line” was the message sent by Garibaldi to Naples after ten hours’ fighting. There had been grave fears expressed by Cavour that the army would march on Rome and expel the French after this conclusion. But the King was advancing toward the south of Italy to prevent any move which would provoke France, and Garibaldi, marching north, dismounted from his horse when he met the Piedmontese, and walking up to Victor Emmanuel, hailed him King of Italy. Naples and Sicily, with Umbria and the Marches, decided in favour of a united sceptre under the House of Savoy. It was Garibaldi’s proclamation to the people which urged them to receive the new King with peace and affection. “No more political colours, no more parties, no more discords,” he hoped there would be from the 7th of November, 1860. It was on that day that the king-maker and the King together entered Naples. Garibaldi refused all the honours which his sword had won, and left for his island-home at Caprera, a poor man still, but one whose name could stir all Europe.
The Italian kingdom was proclaimed by the new Parliament which met in February 1861, at Turin. All parts of Italy were represented save Rome and Venice, and King Victor Emmanuel II entered on his reign as ruler of Italy “by the Grace of God and the will of the nation.”










